Network Impairments
When you're building a codec, camera, or streaming device, you need to know how it behaves before it ships. Does audio glitch at 20ms of jitter or 50ms? Does video freeze gracefully or tear?
Impairments let you find out by injecting delay, jitter, and packet loss into live traffic. Apply controlled conditions, observe the result, find where your system degrades.
Impairments apply to traffic transmitted by the selected interface.
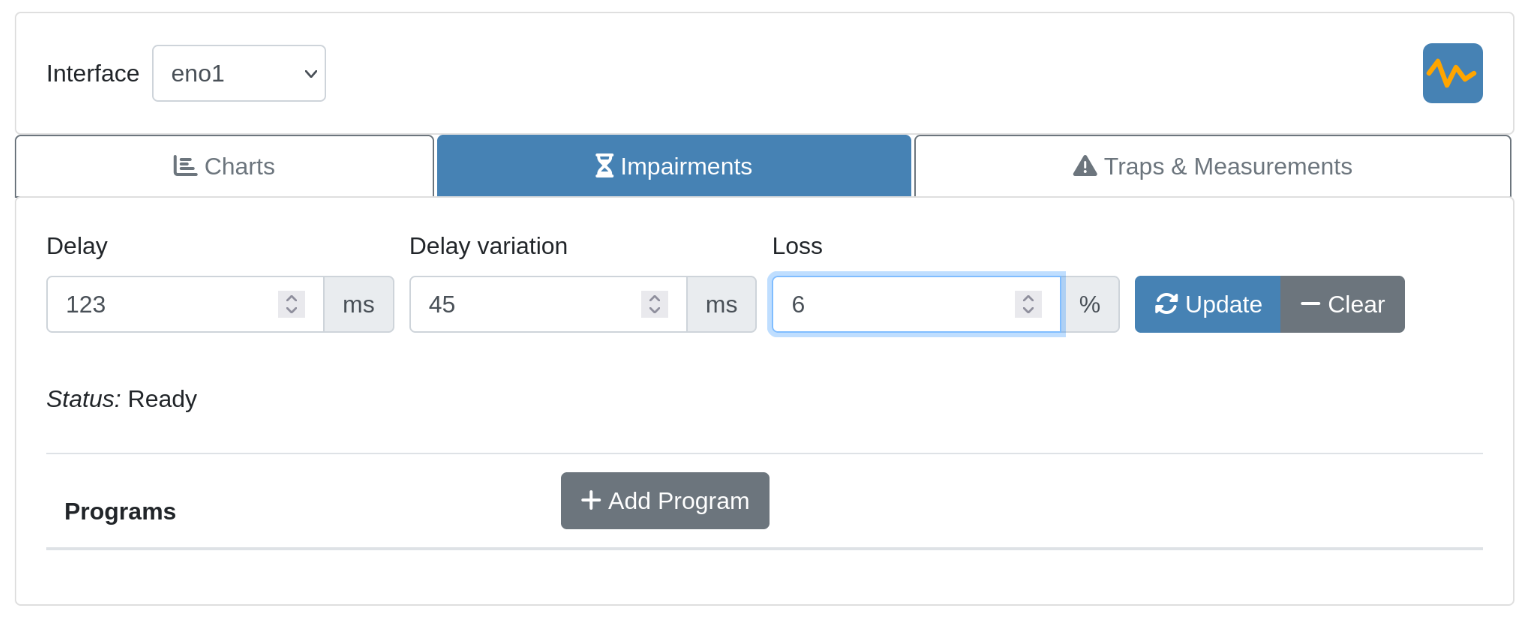
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Delay | Adds fixed latency to every outgoing packet (milliseconds) |
| Jitter | Adds random variation to the delay (±ms) |
| Loss | Randomly drops a percentage of outgoing packets |
Delay
Example: Setting delay to 50ms simulates a network path with 50ms one-way latency (100ms round-trip if applied on both ends).
Jitter
Adds random variation to the delay. Each packet gets the base delay plus or minus a random value up to this amount.
Example: Delay 50ms + Jitter 10ms means each packet is delayed between 40-60ms.
Note: Jitter requires a non-zero Delay value.
Loss
Each packet has an independent chance of being dropped.
Example: 5% loss means each packet has a 5% chance of being dropped.
Programs
Programs script sequences of impairment changes over time. Useful for simulating varying conditions or automating repeatable test sequences.
Example trapezoidal delay profile:
# Ramp up delay, hold, then ramp down
delay=0
sleep 2000
delay=50
sleep 2000
delay=100
sleep 2000
delay=150
sleep 2000
delay=200
sleep 4000
delay=150
sleep 2000
delay=100
sleep 2000
delay=50
sleep 2000
delay=0
Use Add Program to create a new program, then Run to execute it.